Mixing is crucial in pharmaceutical production. This process closely relates to the safety and efficacy of medications. But how do you achieve proper mixing in pharmaceuticals? One key player is high shear mixer. These machines are essential for enhancing pharmaceutical product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Curious about what high shear mixers are and how they work? This blog is meant for you. Today, we will walk through all the essential details about high shear mixers. If you’re thinking of investing in a high shear mixer, reading on will show you why the information we gathered here is worth your time.
What is a High Shear Mixer?
A high shear mixer in pharmaceuticals is used to disperse, emulsify, homogenize, and reduce particle sizes. Whether you’re handling solids, liquids, or even gases, this powder mixing equipment would be a great favor.
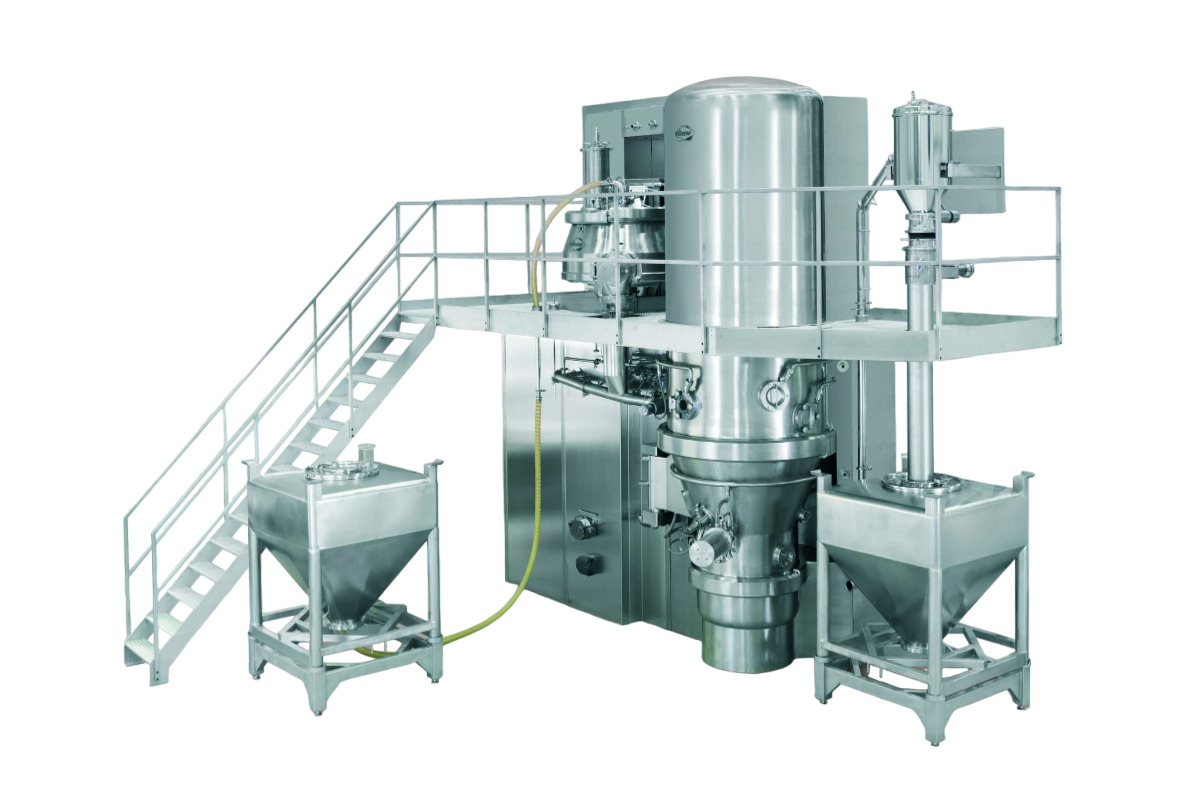
High shear mixers operate at high speeds to generate intense shear forces. The shear can break down particles and finally give you a consistent product. Simply put, a high shear mixer can be a very important processing partner in your pharmaceutical production.
How Does a High Shear Mixer Work?
A high shear mixer uses a motor to spin a shaft with a special mixing head attached. This head has carefully designed blades or rotors. As the rotor spins quickly, it generates a strong shearing action. The material to be mixed gets pulled into the rotor and is then shot out at high speed through openings in a part called the stator.

The mixer creates intense hydraulic shear, turbulence, and sometimes cavitation, which is when tiny bubbles form and collapse. These forces help to break down particles and spread them out evenly.
6 Common Types of High Shear Mixer in Pharmaceuticals
When you’re in the market, you’ll find there are high shear mixers with different configurations. Each has unique advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a closer look at six common types:
1. Inline High Shear Mixer
An inline high shear mixer features a rotor-stator set, creating a continuous flow-through system. It works like a centrifugal pump, continuously pulling ingredients through, which allows for consistent and controlled mixing. These mixers are compact and perfect for integrating into continuous production lines.
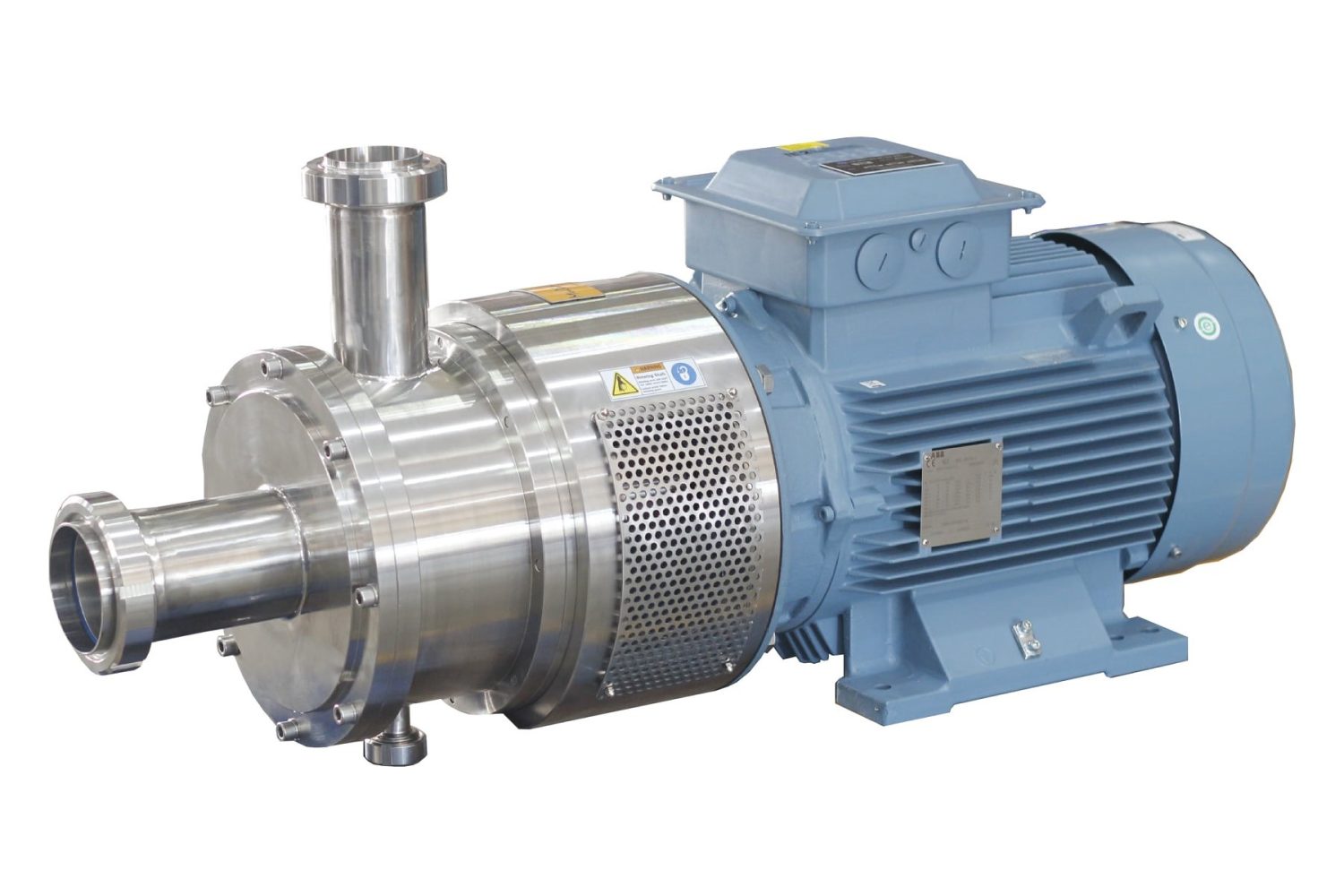

PROS
- Integrates seamlessly into production lines for non-stop mixing.
- Ensures precise control, which is vital for consistent quality.
- Quickly and thoroughly mixes and blends ingredients.
- Compact, easily fitting into existing setups.
CONS
- Only for continuous processes, not for batch mixing.
- Relatively expensive.
- Requires regular maintenance to prevent downtime.
2. Batch High Shear Mixer
A batch high shear mixer allows you to load your ingredients into the mixing chamber from the top. This chamber has a rotor-stator unit with a rotating shaft. These mixers are pretty speedy, processing materials about twice as fast as inline mixers of the same power.
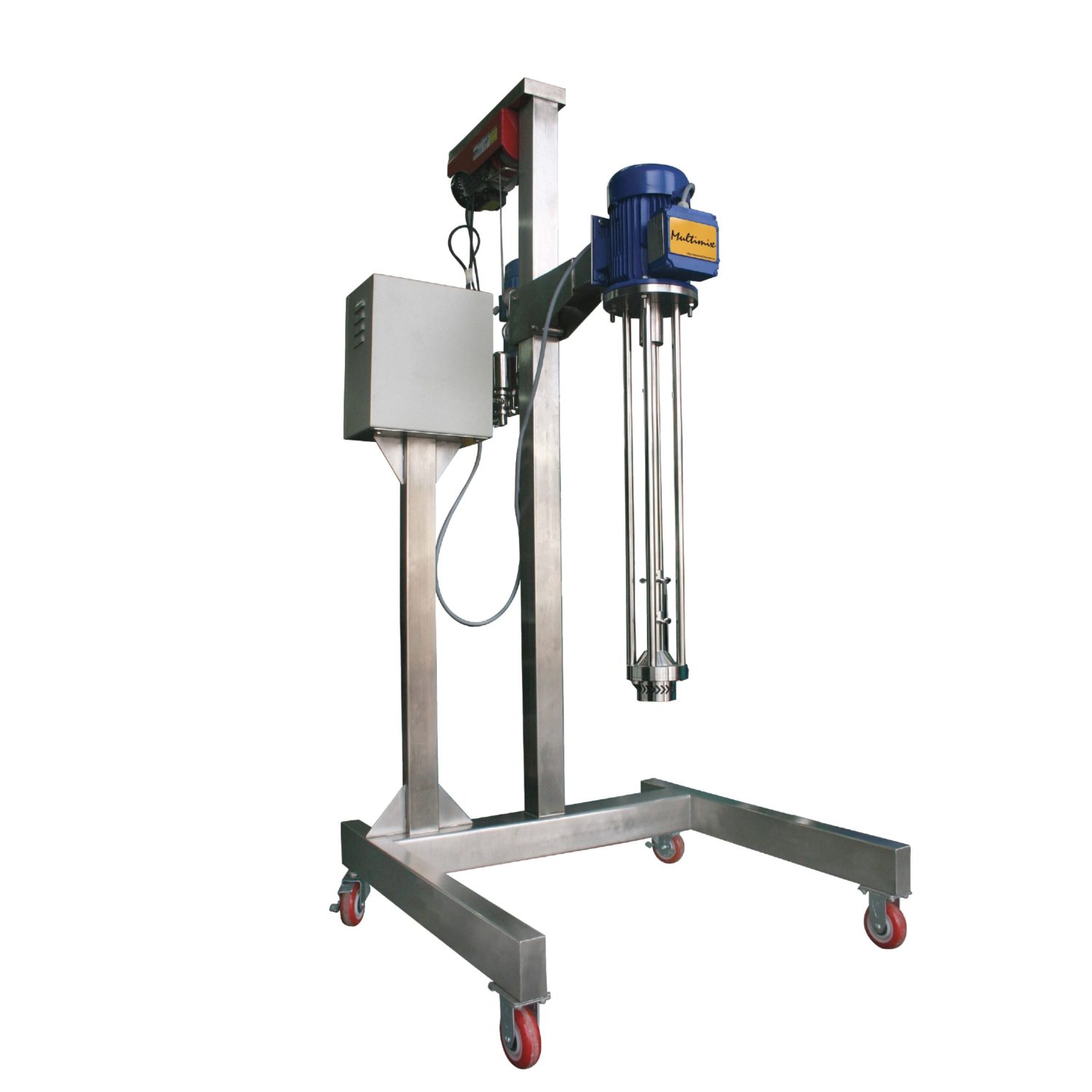

PROS
- Delivers uniform results every time.
- Speeds up blending, homogenizing, and emulsifying.
- Works across various industries and materials.
- Adapts to specific needs and setups.
- Fits well in limited spaces.
CONS
- Only suitable for batch processing, not continuous operations.
- Expensive to buy and maintain, may require expert repair.
- Not easily adjustable to different production sizes.
- Produces significant heat, pressure, and noise, requiring careful handling.
3. Powder Induction Mixer
Powder induction mixers handle inline processing. They come with a vacuum system and a hopper. Also, these mixers feature high-shear tooling. These components work to effectively incorporate powders into the liquid. This method can significantly decrease air entrainment and prevent the formation of clumps.
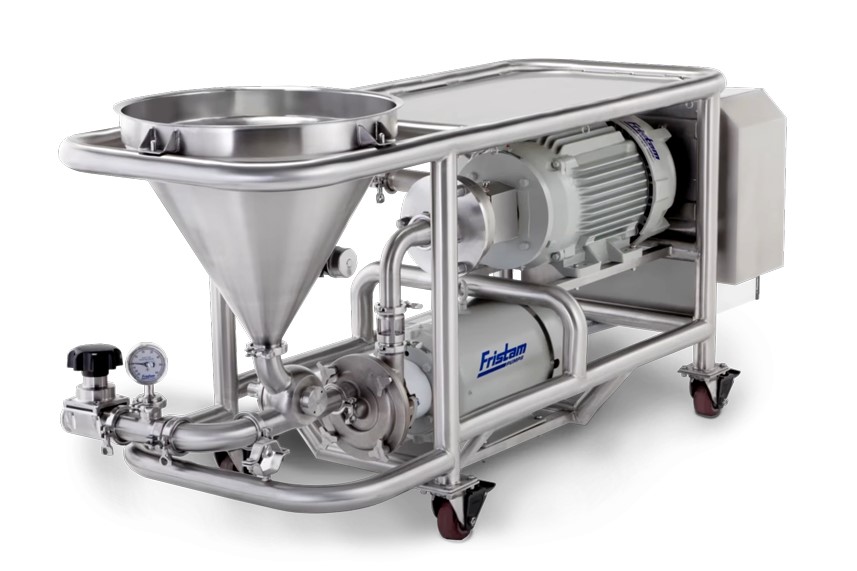

PROS
- Prevents clumping by directly integrating powders.
- Easily movable and adjustable for various mixing needs.
- Lowers physical effort by keeping processes at ground level.
CONS
- Non-Newtonian liquids can unpredictably change in viscosity.
- The heat from mixing may cause unwanted reactions.
- Requires careful control of mixing times and conditions.
4. Bottom Entry High Shear Mixer
Bottom entry high shear mixers are designed to be mounted at the bottom or side of a tank. They are often used alongside slower-moving stirrers. Bottom entry mixers work by drawing in materials with a rotor and stator that are directly connected to a motor, spinning rapidly to create powerful suction and centrifugal forces. This action mills the materials intensely, producing high shearing forces that thoroughly homogenize, emulsify, and disperse the ingredients.
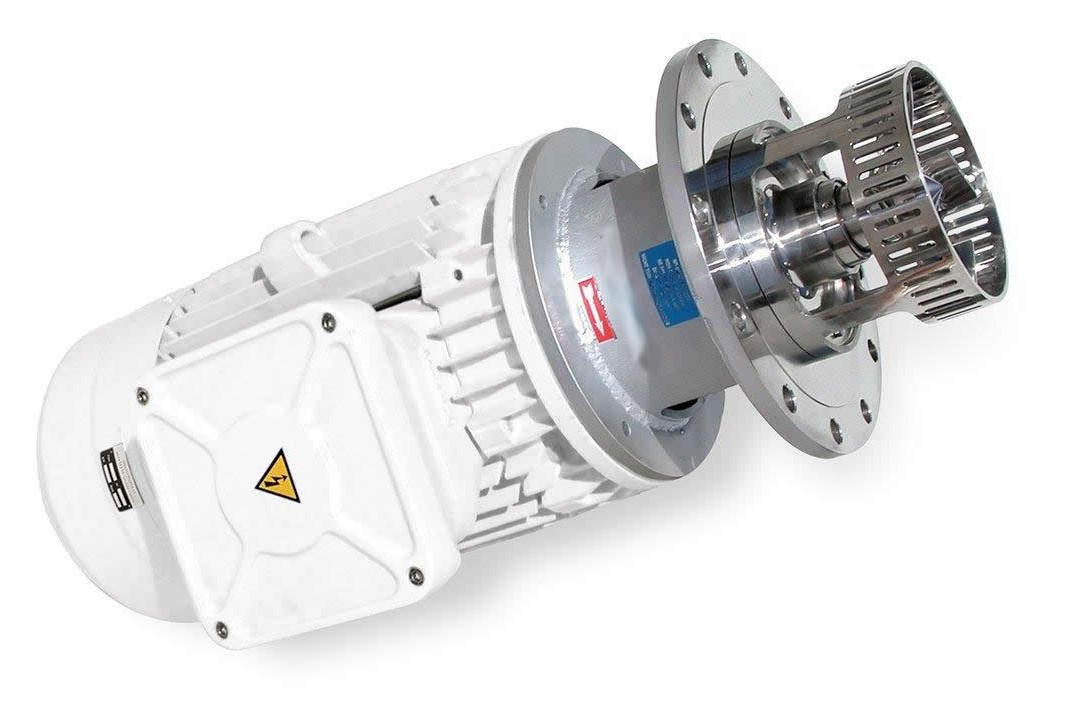
PROS
- Capable of blending to very low levels, especially during drawdown.
- Less risk of contamination.
- Creates a vortex for more effective blending and uniform mixing, even as the tank empties.
- Allows more headroom as no use up space above the tank.
- Easy to clean, maintain, and install due to its bottom placement.
CONS
- Only suitable for mixing within tanks or vessels.
- Requires specific clearances, limiting its use to certain tanks.
- Generally more expensive due to its specialized design and features.
5. High Shear Granulator
High shear granulators transform fine powders into dense granules using a process called wet granulation. This involves mixing the powder with a binding liquid and then agitating the mixture with an impeller to form granules. You can also use dry powders as binders, which melt from the heat created during mixing—this avoids issues like clogging. In typical setups, these high shear mixers work alongside fluid-bed dryers to first refine and then dry the granules, completing the process.
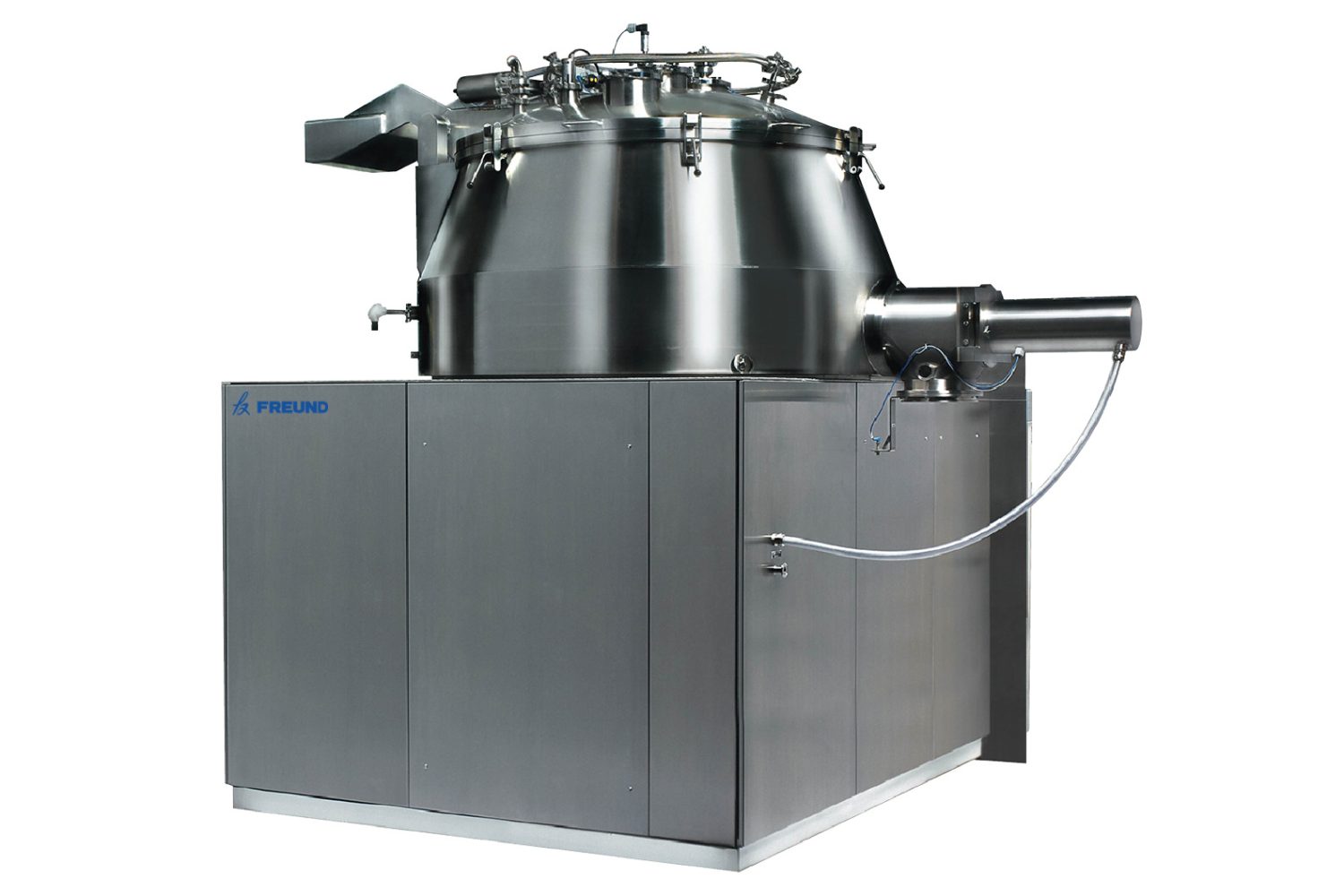

PROS
- Great at breaking down particles and mixing them evenly.
- Uses both wet and dry binders depending on your materials.
- Combines mixing and drying to streamline the production line.
CONS
- The multi-stage process can be tricky to manage.
- The heavy-duty operation can wear out parts, requiring regular upkeep.
- Generally more expensive than simpler machines.
6. Ultra-High Shear Mixer
Ultra-high shear mixers excel in creating smooth, homogeneous mixtures at high speeds up to 15,000 FPM. These mixers can create more intense shear forces than standard mixers. The shearing action can finely disperse solid particles and blend immiscible liquids. This results in mixtures without any clumps or agglomerates. Ultra-high shear mixing technology is capable of producing sub-micron particle sizes. Also, they can process mixtures quickly and efficiently in single or multiple passes.
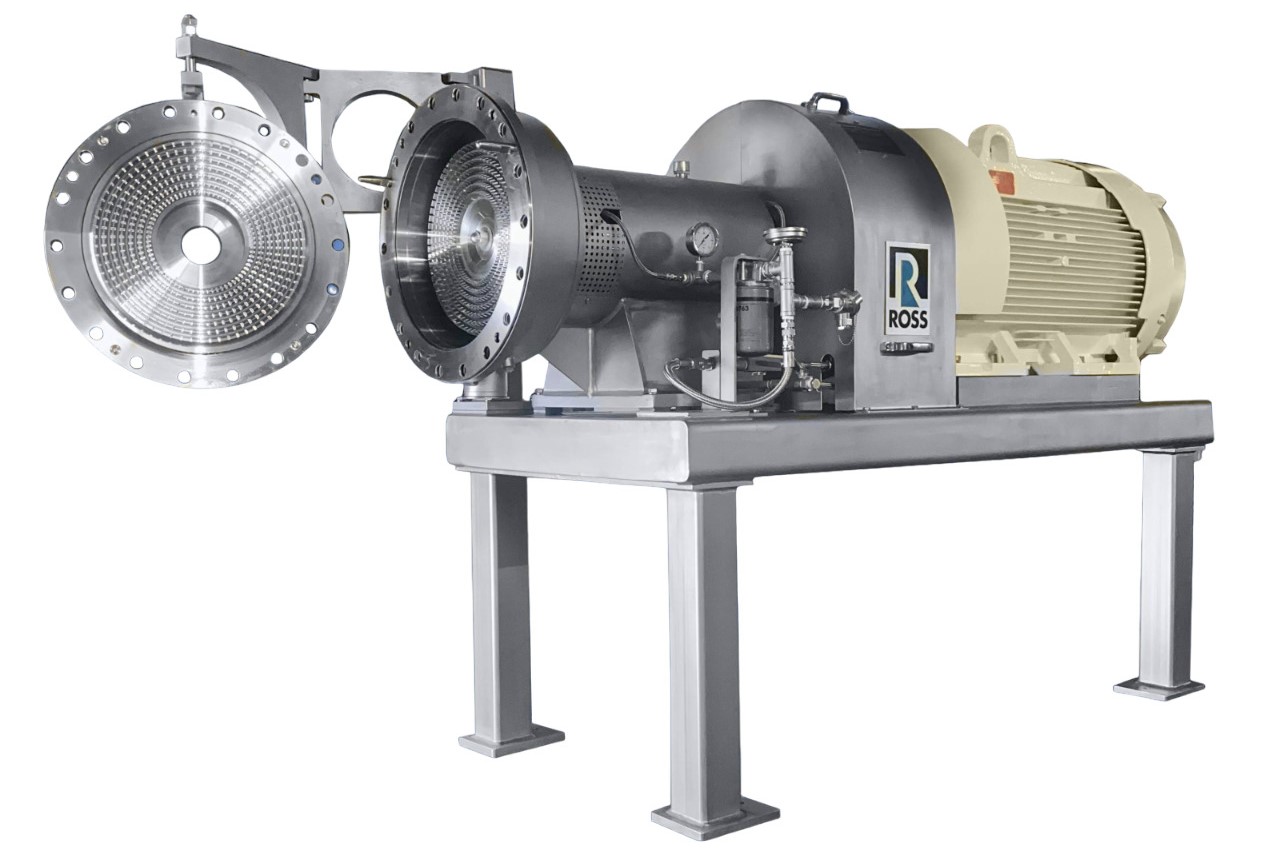

PROS
- Excels at fine dispersions to enhance product stability and smoothness.
- Effectively blends immiscible liquids.
- Ensures uniform product quality across batches.
- Speeds up the mixing process, increasing production efficiency.
CONS
- Consumes a lot of power, increasing operating costs.
- Produces significant heat. Problematic for heat-sensitive materials.
- More effective with smaller batches and less so with larger volumes.
- Can accelerate wear and tear on components.
- Can introduce air, leading to unwanted foaming or aeration.
Applications of High Shear Mixer in the Pharmaceutical Industry
High shear mixers find a wide range of applications in the pharmaceutical industry where they involve carrying out some important tasks such as
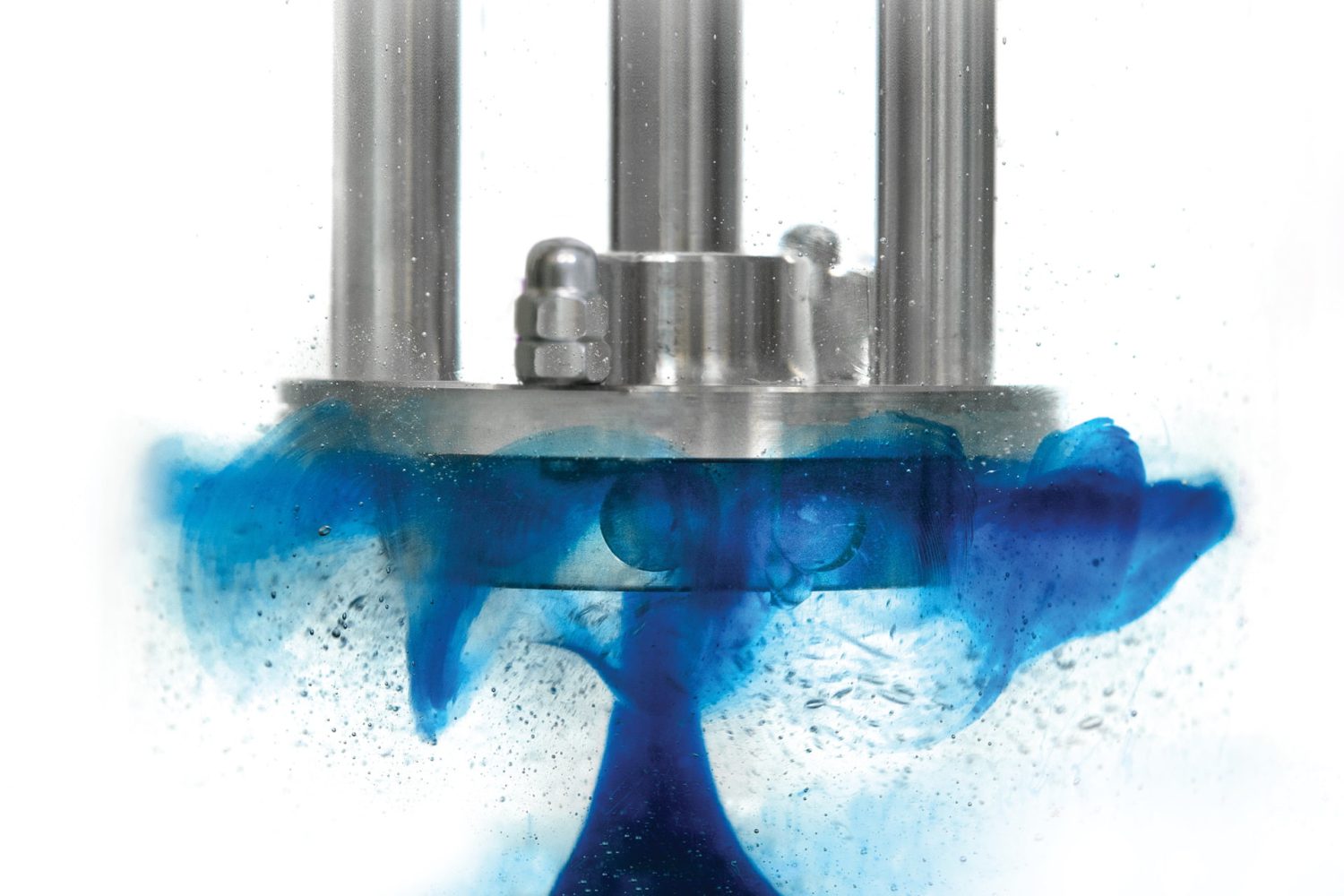
Mixing and Blending
The first and most obvious function of high shear mixers is mixing different substances together. They serve as an efficient manner to allow consistent blending as well.
Particle Size Reduction
The names of these mixers indicate they can produce a shear. This force causes the particles of pharmaceutical products to reduce in size. This results in higher product performance and production efficiency, as well as the broader quality of final products.
Granulation and Wet Milling
These functions are frequently used in pharmaceuticals. In high shear mixers, pharmaceutical powders are milled into smaller particles in order to produce uniform granules. This helps to improve bioavailability.
Dispersion and Deagglomeration
High shear mixers are an excellent choice to uniformly disperse fine powders such as active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients. They may also deagglomerate particles (avoiding caking of the formulation) to achieve drug uniformity and efficacy.
Emulsification
These mixers merge two immiscible fluids in one continuous stable emulsion. The emulsion can be used to make ointments and suspensions.
Homogenization
For liquid substances, high shear mixers will homogenize. As we all know, pharmaceutical formulations are not heat and speed food via an oven. Uniform mixtures are very important when it comes to preparing stable pharmaceutical products.
Nano-Emulsion and Nano-Suspension Formation
Ultra-high shear mixers are most commonly utilized for the formulation of uniformly sized nano-scale emulsions and suspensions. This can result in improved drug delivery or controlled release.
Preparation of Liposome and Vesicle
They also generate liposomes and related vesicles for enhanced drug delivery systems.
FAQs about High Shear Mixers in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing

Q: What’s the difference between a high shear mixer and a regular mixer?
A: Compared to regular mixers, high shear mixers work at higher speeds and generate stronger shear forces. With a high shear mixer, you can get smaller particle sizes and more uniform products.
Q: Can high shear mixers work with any material?
A: High shear mixers are versatile, but they might not be able to process all types of materials. For example, it can be challenging for a high shear mixer to handle extremely dense or highly viscous materials.
Q: Are high shear mixers energy-efficient?
A: In general, high shear mixers can complete mixing in a shorter time. This means they can achieve the same mixing effects with less energy than regular mixers need. However, the specific energy consumption depends upon the specific model and application requirements.
Conclusion
High shear mixers are a game-changer in pharmaceutical manufacturing. They ensure consistent product quality and boost efficiency by using high-speed rotor-stator combos to create intense shear forces, breaking down particles for uniform mixtures. Whether you’re making creams or granules, there’s a mixer type to suit your needs. When picking one, think about your materials, production volume, and budget to find the perfect fit.