Are you frustrated about how to turn your raw powders into perfectly sized granules? No matter what manufacturing industry you’re in, getting the right equipment is half the battle. There’s one machine that can do you a huge favor—a powder granulator.
If you have no idea about this machine, don’t worry! This guide has got you covered. We’ll walk you through everything you need to know about the powder granulator machine. By the end, you’ll feel confident in choosing the right one for your business in 2025. Let’s dive in!
What is a Powder Granulator Machine?
A powder granulator machine is designed to transform powders into granules. Depending on the design, the machine is versatile and operates on different principles.
It can take large powder lumps and break them down into smaller, uniform particles. It can also transform a mixture of fine powders and a liquid binding agent into larger, more manageable particles. The granules created are easier to handle, blend, or process further.
Powder granulator machines are commonly used in applications like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing.
Why You Should Use a Powder Granulator Machine
Using a granulator machine can really boost your manufacturing process in several ways. Here are some solid reasons to give it a thought:

- Fine powders can be messy and hard to handle. Granules are larger and flow much better, making them simpler to process.
- Granules are uniform in size and shape. This is especially important in the manufacture of medicine.
- Powders are fine and dry, so they can easily become airborne and cause flying dust. Turning powders into granules reduces dust. This makes the workspace safer for workers and minimizes material loss.
- Granules flow more easily through machinery, preventing jams and keeping production lines running smoothly.
- When ingredients are granulated, they mix more evenly, ensuring each product batch is consistent. They also become more stable and easier to compress.
- Improved handling, reduced waste, and efficient production can save you time and money.
Types of Powder Granulation Processes
The powder granulation methods available today can be generally classified into two types:
1. Wet Granulation Process
Wet granulation, as the name suggests, involves adding liquids. This method often uses a binder solution to promote adhesion between the powder particles. Common binders are water, alcohol, starch, sugars, and other non-toxic synthetic polymers. Since the formed granules are wet, a drying step is required in this method. Wet granulation is a preferred method when preparing ingredients for making tablets or capsules.
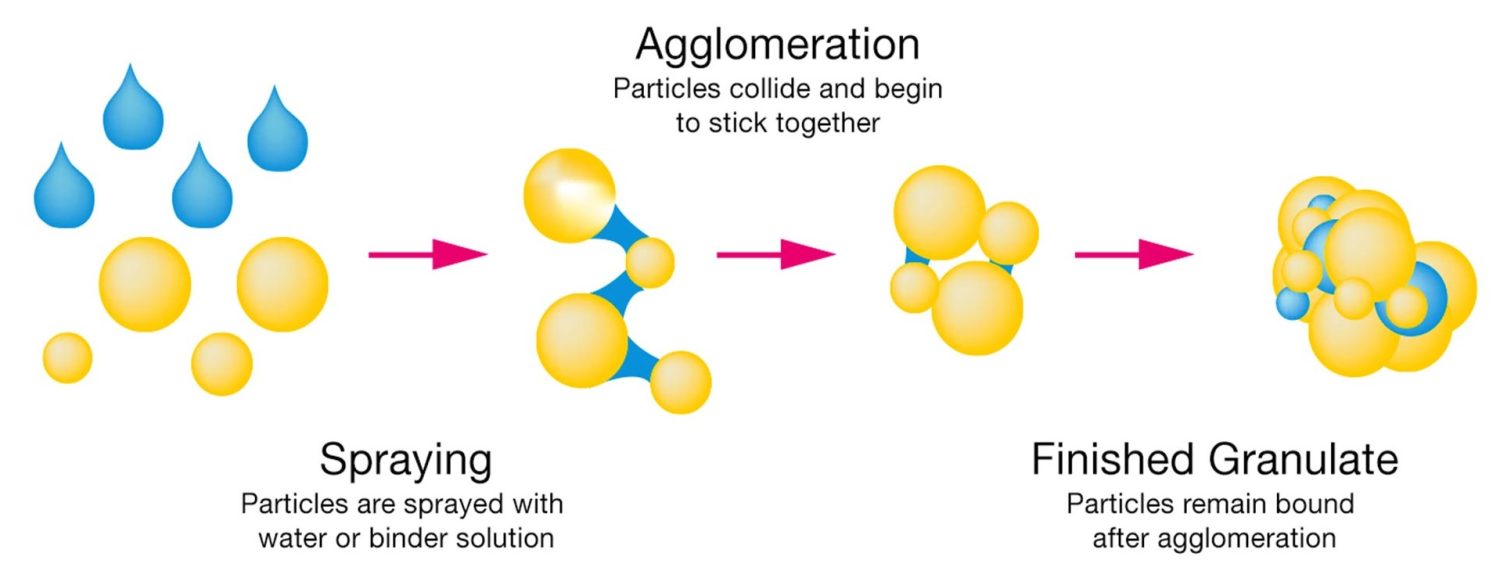
Wet granulation can be done in a few different ways. Here are the main types:
a. High Shear Wet Granulation
This is the most commonly used technique. The powder is combined with a binder in the granulator that mixes everything at high speeds. The high shear forces, created by an impeller and a chopper, break down the mass and form the granules just the right size.
b. Low Shear Wet Granulation
If you’re working with more fragile materials, low shear wet granulation is the way to go. This method uses slower speeds and gentler mixing forces. So, the granules tend to be bigger and less dense.
c. Fluidized Bed Wet Granulation
This one is a bit of a multitasker. A fluidized bed granulator actually combines granulation and drying in one process. The powder floats in the air inside the chamber. The binder solution is sprayed on the powder particles. The air dries up the particles as they form granules.
2. Dry Granulation Process
This process doesn’t involve liquids or high temperatures. If you’re handling moisture or heat-sensitive ingredients, this method is your go-to. Essentially, dry granulation makes your powder easier to process further down the production line.
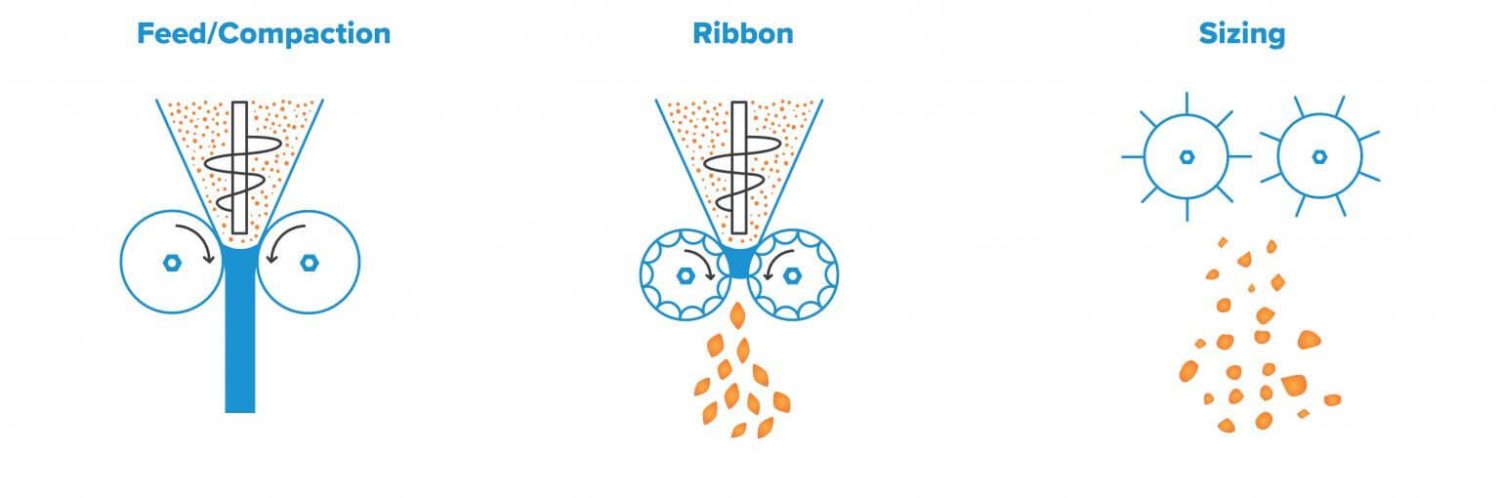
Dry granulation can be performed in two approaches, depending on the equipment used:
a. Roller Compaction
This technique works by auger feeding the powder into the gap between two counter-rotating rollers. As the rollers rotate, they apply high pressure to the powder, forming a ribbon. The ribbon is then milled and sifted for granules.
b. Slugging
In this process, the powder is first compressed into large, flat slugs using a tablet press. The slugs are then milled into granules. This method is cost-effective, but it’s less commonly used today. This method cannot ensure the size and hardness of each slug is consistent.
Common Powder Granulator Machine Types
Now, it’s time to explore what powder granulator options are out there. Based on the granulation processes we’ve discussed, some powder granulator machines are designed for specific tasks, while others are versatile multitaskers. Let’s check them out!
Here are a few types of machines typically used to carry out the wet granulation process:
Low Shear Mixer
A low shear mixer is used when you need a gentle touch for your ingredients. It mixes powders and liquids at a slower speed, which helps keep delicate materials intact and prevents them from getting damaged.

How it works: The powder is added to the mixer, and a slow-moving impeller or blade mixes the ingredients. The binder is then added gradually, helping the particles stick together to form granules.
Pros:
- Perfect for delicate powders that might break apart with too much force.
- Good at creating a smooth, consistent mixture without overworking the ingredients.
- Uses less power because it operates at lower speeds.
Cons:
- Might take longer to form granules.
- Not ideal for high-density materials.
Fluidized Bed Granulator
This powder granulator machine is a two-in-one granulator-dryer combo. This means that the granulation and drying processes can be carried out at the same time. It’s highly efficient, especially when you need to process large volumes of materials in a continuous flow.

How it works: The powder is suspended in a stream of air (fluidized), and the binder is sprayed on top, creating granules. The air also helps dry the granules as they form, so you get both granulation and drying in one step.
Pros:
- Combines granulation and drying, saving time and space.
- The fluidized air helps dry the granules evenly as they form.
- Ideal for continuous processing of large batches.
Cons:
- Can be a bit tricky to set up, operate, and maintain.
- Tends to be more expensive than other machines due to their multi-functionality.
For dry granulation, common granulation machines are:
Roller Compactor
A roller compactor is the most popular machine used in dry granulation. It works by pressing dry powder between two rollers to form solid ribbons, which are then broken into smaller granules.
How it works: The powder is fed into the machine, and the rollers apply pressure to compress it into ribbons. These ribbons are then milled and pass through a sieve to become granules.
Pros:
Can handle large amounts of material quickly.
Works well with a variety of powders, including those sensitive to moisture and heat.
Great for materials that can’t tolerate wet conditions.
Cons:
- The space between the rollers and compaction pressure must be carefully managed.
- May produce small particles that might need to be screened out.
Oscillating Granulator
This powder granulator machine breaks large lumps into smaller particles by using a back-and-forth motion with an oscillating rotor. It also features a sieve to screen out the granules of the desired size.
How it works: Powder lumps go into the oscillating granulator. The rotor shreds them into smaller, uniform particles. A sieve mounted under the rotor then sorts out the right-sized granules.
Pros:
- Ensures that the granules are consistent in size.
- Facilitates fine-tuning of granule size by altering the sieve.
- Gentle on fragile and delicate materials.
Cons:
- Usually slower compared to the roller compactor.
- May take more time on cleaning and maintenance due to the complex designs of the rotor and sieve.
Key Factors to Consider Before Buying a Powder Granulator Machine
- Material Type and Properties: Think about the type of material you’ll be granulating. If your material is heat-sensitive, a wet granulation machine might not be the best fit since it involves drying.
- Granule Size and Consistency: Choose a machine that can produce the desired granule size. Machines with adjustable screens or milling systems give you more flexibility here.
- Production Volume: How much do you need to produce? Different granulation machines are better suited for different production volumes. If you’re just starting out, a smaller, batch-style machine may be more practical.
- Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance: Powder granulator machines can be a bit messy. Choose machines with easy-to-clean parts, especially if you’re working with sticky or wet materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for energy-efficient machines that help cut down on operating costs. Machines with adjustable speeds or energy-saving features are a plus.
- Budget: While it’s tempting to go for the cheapest option, keep in mind the long-term costs. Granulation machines vary in price. Fluidized bed granulators tend to be pricey but might save you money in the long run by combining granulation and drying.
- Space and Layout: Measure your available space before you shop. Ensure there’s sufficient space for the equipment. You’ll also want to factor in any additional equipment like dryers or mills.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the machine meets industry standards (like GMP or FDA) if you’re in a regulated industry, such as pharmaceuticals or food.
Leading Powder Granulator Machine Brands in 2025
To help you save time on research, we’ve put together a list of reputable powder granulator machine manufacturers from around the world. If you’re unsure where to start, check them out!
| Company | Country | Powder Granulator Machine Features |
| GEA Group | Germany | – Combines mixing, granulation, drying, and tableting in one system. |
| – Customizable and modular design for scalable production. | ||
| – Safe and clean design, ideal for small amounts of potent compounds. | ||
| L.B. Bohle | USA | – Handles granulation, coating, and drying without reconfiguration. |
| – Compact, space-saving design with efficient product transfer. | ||
| – Advanced real-time moisture measurement for better control. | ||
| ACG Group | India | – Faster processing with consistent particle size and mix quality. |
| – Compact design and closed-loop systems for efficient material handling and minimal dust. | ||
| – Advanced control system for easy monitoring and industry compliance. | ||
| Fitzpatrick | Canada | – Locks in blends and improves powder flow for smoother tablet production. |
| – Scalable from lab to full production, with consistent pre-compression and roll control. | ||
| Anxine | China | – Ideal for high-viscosity materials and moisture/heat-sensitive granulation. |
| – Cost-efficient with GMP standards and flexible production options. | ||
| FREUND | USA | – Versatile roller compaction for uniform, dense sheets in dry granulation. |
| – Easy to use, simple to clean, and cost-effective with a focus on processing efficiency. | ||
| Romaco Innojet | Germany | – Combines drying, granulation, and coating in one system with user-friendly software for easy scale-up. |
| – Compact, mobile design with advanced cleaning systems and dust-free operation. | ||
| IMA Group | Italy | – Offers a dust-free and contamination-free granulation process. |
| – Features a unique impeller design that avoids product sticking. | ||
| – Easy integration with other equipment and interchangeable modules for different batch sizes. | ||
| Fluid Air | USA | – Fluid bed systems with consistent performance and modular inlet/exhaust systems for efficient setup. |
| – Features like explosion-proof systems and recipe-based controls for customization. | ||
| Gansons | India | – High-shear granulators with multiple impellers for uniform granulation. |
| – Compact, integrated systems for easy scaling and minimal downtime. | ||
| – Plug-and-play simplicity, reducing cross-contamination risks. |
Key Takeaways:
- GEA and IMA are ideal for high-volume, integrated systems with flexibility and safety.
- L.B. Bohle and Romaco Innojet are great for compact, customizable setups that transition well from lab to full-scale production.
- Fitzpatrick and FREUND focus on precision, scalability, and ease of use, with solid options for both dry and wet granulation.
- ACG Group and Fluid Air stand out for their compact, efficient, and customizable solutions with advanced controls.
- Anxine and Gansons offer cost-effective, flexible machines with excellent performance for various types of granulation.
Wrap-Up
As we head into 2025, picking the right powder granulator machine is key to boosting your production and product quality. Keep in mind those important factors when searching for your best fit. Also, don’t forget to check out reliable manufacturers. With the right granulator, you’ll be ready to tackle whatever comes your way in the industry.